Audio optimization
The following chapters describe the software and hardware optimization solutions of AmebaPro2 audio.
Audio setting
Gain setting
Analog microphone gain setting
The audio analog input gain can be namely divided into analog gain and digital gain.
Analog mic gain
It supports 0, 20, 30, 40 dB for the gain optimization.
User can use audio_mic_analog_gain or set the parameter mic_gain for audio module to set it.
ADC gain can be used to set the input (analog to) digital gain – ADC Volume.
The range is -17.625dB (0x00) ~ 30dB (0x7F)
User can use the function audio_adc_digital_vol or use CMD_AUDIO_SET_ADC_GAIN to control audio module to use the function.
A digital gain configuration is offered to control the audio output gain. Customers can set a reasonable gain value via DAC Volume to obtain the appropriate audio output volume according to their needs. Basically setting the gain to 0dB (0xAF), the output amplitude will meet the board audio output volume requirements. Note that a sound breakage will happen when the output gain is setting too large.
If the analog gain is too large, analog gain will affect the sound effect and noise will be obvious.
Recommend that customers can first configure the digital gain. If the audio signal gain need to increase but the digital gain achieves the maximum range, then configure the analog gain.
Digital microphone gain setting
Left mic gain
Left dmic gain and it supports 0, 12, 24, 36 dB for the gain optimization.
User can use audio_l_dmic_gain or set the parameter dmic_l_gain for audio module to set it.
Right mic gain
Right dmic gain and it supports 0, 12, 24, 36 dB for the gain optimization.
User can use audio_r_dmic_gain or set the parameter dmic_r_gain for audio module to set it.
Speaker gain setting
DAC gain can be used to set the output digital (to analog) gain – DAC Volume.
The range is -65.625dB (0x00) ~ 0dB (0xAF)
User can use the function audio_dac_digital_vol or use CMD_AUDIO_SET_DAC_GAIN to control audio module to use the function.
HPF setting
In AmebaPro2, it provides a high pass filter for user to filter the low frequency noise. This is use to filter out the noise filter for DC power, sugget to set default value 0. If user want to use other filter, please refer to EQ setting.
Here is the function:
void audio_adc_l_hpf(audio_t *obj, BOOL en, audio_hpf_fc hpf_fc);
The parameters mean:
obj: Audio object define in application software.
en: enable the high pass frequency or not.
hpf_fc: set the cutoff frequency, the value is from 0~7; fc ~= 5e-3 / (hpf_fc + 1) * fs.
EQ setting
In AmebaPro2, it also provides five sets of biquad filters in three sides for left digital mic (analog mic), right digital mic and audio output.
One biquad filter can switch to high-pass, low-pass, band-pass, notch, peak, low shelf, and high shelf filter by register settings.
Here are some tips for user to use the EQ:
Select the biquad filter
User can use the following websites to configure the preferred filter type, sample rate, cutoff frequency, Q value and Gain first:
https://www.earlevel.com/main/2021/09/02/biquad-calculator-v3/
Get the registers’ value of selecting filter
User can use AmebaPro2_EQ_tool.exe to generate register settings. For example, if we choose a high pass filter with cutoff frequency 200Hz and Q value 0.707, user can type the setting and get the registers’ value (0x1e45618, 0x1c000000, 0x2000000, 0x3c72d61, 0x1e35d500) for this setting.
Figure EQ setting
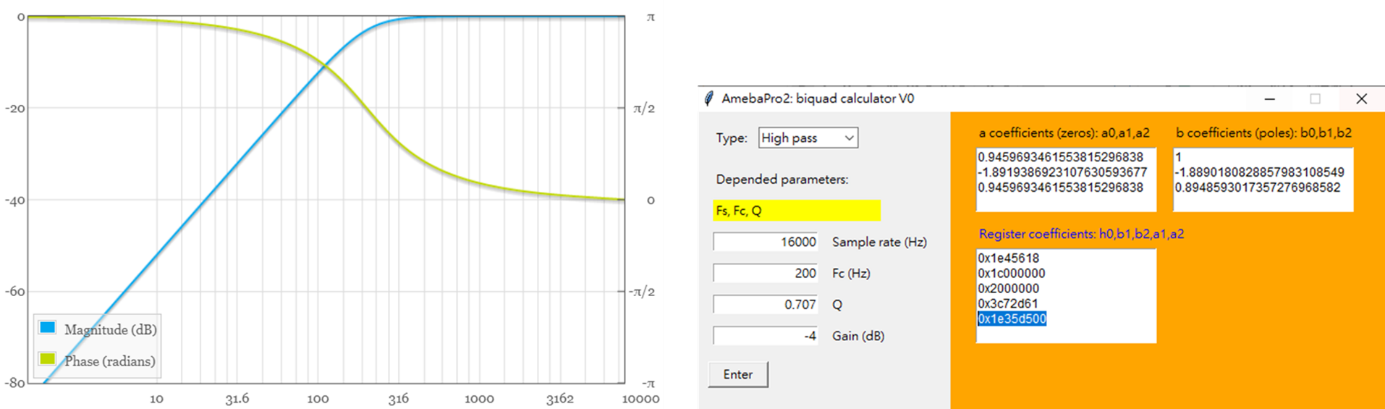
Set the register value got from AmebaPro2_EQ_tool.exe
After getting the registers’ value, user can use the following functions to apply the filter setting on AmebaPro2 on left digital mic (analog mic), right digital mic and audio output. Note that there are 5 filters could be set in each side. User could also set the EQ parameters in audio_params_t when using the MMF setting.
void audio_input_l_eq(audio_t *obj, audio_eq eq, BOOL en, u32 h0, u32 b0, u32 b1, u32 a0, u32 a1);
void audio_input_r_eq(audio_t *obj, audio_eq eq, BOOL en, u32 h0, u32 b0, u32 b1, u32 a0, u32 a1);
void audio_output_l_eq(audio_t *obj, audio_eq eq, BOOL en, u32 h0, u32 b0, u32 b1, u32 a0, u32 a1);
Here are the parameters:
obj: Audio object define in application software.
eq: Select the EQ number, can be 0~4.
en: enable the eq filter or not
h0, b0, b1, a0, a1: the registers’ value gotten from AmebaPro2_EQ_tool.exe.
Other setting
Here are some commands about the module audio setting:
CMD_AUDIO_SET_RESET
will be re-initialize the audio setting and also the ASP algorithms. If you do some changes need to reset the audio configuration, like change the sample rate, reset the audio to switch the configuration.
CMD_AUDIO_SET_SAMPLERATE
can set the sample rate. After using this command, a reset is needed to apply the sample rate configuration on audio and ASP algorithms.
Note
If using audio codec, be sure the sample rate is fitting the sample rate used in audio codec.
CMD_AUDIO_SET_TRX
Provide a way to stop and re-start the audio without re-initialize the audio system and ASP algorithms. Set 0 to stop the tx and rx progresses or 1 to start them.
CMD_AUDIO_SET_MIC_ENABLE/CMD_AUDIO_SET_SPK_ENABLE
Mute or unmute the mic input/speaker output. This command will not open or close the audio codec, but set the digital data to zero.
Audio ASP algorithm
The following table shows some common audio problem with their causes and also the adjustment using ASP algorithm.
Situation |
Algorithm |
Influence End |
Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
Distortion |
AGC |
transmitting end |
|
Low audio volume |
AGC |
transmitting end |
|
Echo or howling |
AEC |
transmitting end |
|
Intermittent voice |
AEC、NS |
transmitting end |
|
Noise floor |
NS |
transmitting end |
|
Mechanical sound |
Network、Device |
Receiving end |
|
Note
The audio signal processing (ASP) is based on the digital audio signal. If the audio signal has already has the distortion, the ASP has no promise to get the expected result.
Open ASP algorithm
For using ASP algorithm, user need to turn off the new library by –DBUILD_CT=off. For example, cmake .. -G”Unix Makefiles” -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=../toolchain.cmake –DAUDIO_TEST_TOOL=on.
The codes and functions related to the ASP algorithm are shows in the table.
Enable ENABLE_ASP in module_audio.h and use the 3A (AGC: Automatic gain control; ANS: Adaptive noise suppression; AEC: Acoustic echo cancellation) algorithms to obtain better audio effects.
Note
The parameters, sample_rate and mic_gain, and the initialization of NS, AEC, AGC and other algorithms will be setting at CMD_AUDIO_APPLY and CMD_AUDIO_SET_RESET.
To enable ASP function user can use the following parameters in ASP.h:
=================== Open ASP algorithm (ASP.h) ================
typedef struct CTNS_cfg_s {
int16_t NS_EN;
int NSLevel;
int16_t HPFEnable;
int16_t QuickConvergenceEnable;
int16_t Reserve1;
} CTNS_cfg_t;
typedef struct CTAGC_cfg_s {
int16_t AGC_EN;
CT_AGC_MODE AGCMode;
int16_t ReferenceLvl;
int16_t RatioFormat; // Ratio format: 0 => integer, range 1~50, 1 => 8.8 fix point, range 26~50*256 (mapping 26/256~50)
int16_t AttackTime;
int16_t ReleaseTime;
int16_t Ratio[3];
int16_t Threshold[3]; // Threshold1, Threshold2, NoiseGateLvl
int16_t KneeWidth;
int16_t NoiseFloorAdaptEnable;
int16_t RMSDetectorEnable;
int16_t MaxGainLimit;
} CTAGC_cfg_t;
typedef struct CTAEC_cfg_s {
int16_t AEC_EN;
int16_t EchoTailLen;
int16_t CNGEnable;
int16_t PPLevel;
int16_t DTControl;
int16_t ConvergenceTime;
int16_t Reserve1;
} CTAEC_cfg_t;
typedef struct VQE_SND_STATE_s {
int16_t DoA; //in degrees
int16_t ERLE; //in dB
int16_t SinLvldB; //in dBFs
int16_t SoutLvldB; //indBFs after AGC (if AGC is enabled)
int16_t DTState; //0 = single talk or 1 = doulble talk
int16_t HCDetectState; //1 = detected, 0 = not detected
uint8_t AECRun;
uint8_t AGCRun;
uint8_t NSRun;
uint8_t BFRun;
uint8_t Reserve1;
uint8_t Reserve2;
uint8_t Reserve3;
uint8_t Reserve4;
} VQE_SND_STATE_t;
typedef struct VQE_RCV_STATE_s {
int16_t RinLvldB;
int16_t RoutLvldB;
int16_t HCDetectState; //1 = detected, 0 = not detected
uint8_t AGCRun;
uint8_t NSRun;
uint8_t Reserve1;
uint8_t Reserve2;
uint8_t Reserve3;
uint8_t Reserve4;
} VQE_RCV_STATE_t;
The following is detail of the parameters in each configuration
configuration |
Parameters |
|---|---|
CTAEC_cfg_t |
|
CTAGC_cfg_t |
|
CTNS_cfg_t |
|
CTBF_cfg_t |
|
(plan to support the function) |
|
The following is detail of the information structure for the RCV (Mic) and SND (Speaker) part
configuration |
Parameters |
|---|---|
VQE_SND_STATE_t |
|
VQE_RCV_STATE_t |
|
In “ASP.h” it defined some function for the ASP setting. The following table shows the functions for setting the ASP algorithm:
Function |
Related module |
Parameters |
Note |
|---|---|---|---|
AEC_init |
NS, AEC, AGC |
|
|
AEC_set_level |
AEC |
|
|
NS_set_level_for_AEC |
NS |
|
|
AEC_set_runtime_en |
AEC |
|
|
AEC_process |
NS, AEC, AGC |
|
|
AEC_destory |
NS, AEC, AGC |
|
|
AGC_init |
AGC |
|
|
AGC_process |
AGC |
|
|
AGC_destory |
AGC |
|
|
NS_init |
NS |
|
|
NS_process |
NS |
|
|
NS_destory |
NS |
|
|
VQE_SND_init (not support yet) |
NS, AEC, AGC,BF |
||
VQE_SND_process (not support yet) |
NS, AEC, AGC,BF |
||
VQE_SND_destory (not support yet) |
NS, AEC, AGC,BF |
ASP algorithm usage
Here are the configurations for ASP algorithm:
8K and 16K audio sample rate are supported in the ASP algorithms.
The default ASP settings - default_rx_asp_params and default_tx_asp_params are defined in module_audio.c.
Users can use CMD_AUDIO_GET_RXASP_PARAM and CMD_AUDIO_GET_TXASP_PARAM to get the ASP parameters for RX and TX ASP parameters in the audio module.
Users can use CMD_AUDIO_SET_RXASP_PARAM and CMD_AUDIO_SET_TXASP_PARAM to set the ASP parameters for RX and TX ASP parameters.
When default_rx_asp_params.agc_cfg.AGC_EN and default_tx_asp_params.agc_cfg.AGC_EN set 0 which means disable the AGC process in RX and TX direction, while 1 means enabling the AGC process. When default_rx_asp_params.ns_cfg.NS_EN and default_tx_asp_params.ns_cfg.NS_EN set 0 which means disable the NS process in RX and TX direction, while 1 means enabling the NS process.
When default_rx_asp_params.aec_cfg.AEC_EN set 0 which means disable the AEC process in RX direction, while 1 means enabling the AEC process.
AEC setting
The AEC algorithm includes three parts: delay adjustment strategy, linear echo estimation, and nonlinear echo suppression.
Use CMD_AUDIO_RUN_AEC to dynamically switch the use of AEC_process().
Use CMD_AUDIO_SET_AEC_ENABLE to determine whether AEC_init() is enabled during audio reset.
CMD_AUDIO_SET_AEC_LEVEL can set the strength of cancellation.
NS setting
The NS algorithm is aimed at decrease the noise or environment sound, so it is recommended to use before other ASP algorithms.
Use CMD_AUDIO_SET_NS_ENABLE to determine whether NSx_init() is enabled during audio reset.
Use CMD_AUDIO_RUN_NS to dynamically switch the use of NSx_process().
AGC setting
The AGC algorithm is used to balance the audio volume of signal streaming.
Use CMD_AUDIO_SET_AGC_ENABLE to determine whether AGC_init() is enabled during audio reset.
Use CMD_AUDIO_RUN_AGC can dynamically switch the use of AGC_process().
Audio test tool
AmebaPro2 provide an example for audio testing.
User can use the following steps to build up the audio test tool image
Step1: cd project\realtek_amebapro2_v0_example\GCC-RELEASE
Step2: mkdir build
Step3: cd build
Step4: cmake .. -G”Unix Makefiles” -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=../toolchain.cmake
–DAUDIO_TEST_TOOL=onStep5: cmake –build . –target flash
The following shows the command of the test tool
Common command
command |
parameters |
description |
|---|---|---|
AUMMODE |
|
Set up the microphone type |
AUMG |
|
Set up the analog mic gain (0: 0dB, 1: 20dB, 2: 30dB, 3:40dB) |
AUMB |
|
Set up the mic bias (0: 0.9, 1: 0.86, 2: 0.75) |
AUMLG |
|
Set up the left digital mic (0: 0dB, 1: 12dB, 2: 24dB, 3:36dB) |
AUMRG |
|
Set up the right digital mic (0: 0dB, 1: 12dB, 2: 24dB, 3:36dB) |
AUADC |
|
Set up audio input digital gain level, the gain level is up 0.375dB/step. The max and min gains are 30dB and -17.625dB. |
AUMICM |
|
Mute MIC or not |
AUSR |
|
Set up the audio input and output sample rate. |
AUMLEQ |
|
Set up the EQ for analog or left digital microphone (PDM rising trigger). There are 5 EQs ([eq num]) can be used (the EQ0 is used for a HPF default). The register setting can generate by AmebaPro2_EQ_tool.exe. |
AUMREQ |
|
Set up the EQ for right digital microphone (PDM falling trigger). There are 5 EQs ([eq num]) can be used (the EQ0 is used for a HPF default). The register setting can generate by AmebaPro2_EQ_tool.exe. |
AUMICEQR |
Reset the mic EQ without re-initializing the audio module |
|
AUHPF |
|
Set HPF cutoff frequency fc ~= 5e-3 / (cutoff num + 1) * fs, 0 means 40Hz @ fs 8kHz, 80Hz @ fs 16kHz). This is use to filter out the noise filter for DC power, sugget to set default value 0. If users want to use other filter, please refer to AUMLEQ and AUMREQ. |
AUSPEQ |
|
Set up the EQ for audio output. There are 5 EQs ([eq num]) can be used (the EQ0 is used for a HPF default). The register setting can generate by AmebaPro2_EQ_tool.exe. |
AUSPEQR |
Reset the speaker EQ without re-initializing the audio module |
|
AUDAC |
|
Set up the audio output digital gain, the gain level is up 0.375dB/step. The max and min gains are 0dB and -65.625dB. |
AUSPM |
|
Mute the audio output ([enable_mute]=1) or unmute the audio output ([enable_mute]=0). |
AUTXMODE |
|
Set up the audio output mode, there are four modes supported now. The noplay mode will stop sending data to audio output .The playmusic mode will start to play the music (support 8k or 16k). The playback mode will audio input will directly send to audio output. The audio tone mode will start playing the audio tone setting by [audio_tone(Hz)]. |
AUDRST |
Reset the ram disk table. Enter this command after put external file into the ram disk |
|
AUAMPIN |
|
Set up or down the audio amplifier pin. |
TONEDBSW |
[sweep_DB_interval(ms)] |
Enable the dB sweep when play tone |
AUTRX |
|
Set down or up the audio input and output. |
AUMSGS |
|
set the audio message show level
|
AURES |
|
Reset the audio module to enable the previous audio setting. |
AUFFTS |
|
Enable print audio input FFT result, but the play back mode is not supported. |
AUINFO |
Get the current setting parameters, libraries’ version and ASP run status |
|
P2PEN |
|
When enabling this operation, users can use AURXP2P command and AUTXMODE=playstream |
AURXP2P |
|
Open the audio to APP audio streaming |
AUFILE |
|
Set up the audio save file name. The legth |
AUREC |
|
Start record the audio data for record time. RECORD_TYPE can select to save RX (audio input), TX (audio output before ASP) and ASP (audio input after ASP), TXASP(audio output after ASP). |
AUCOPY |
|
Set the audio file will be copied to other storage place after each record. NOCOPY: just save in RAM TFTP: copy through tftp server SD: copy to the SD cardEnable the save file download to SD card or not. If enabling the SD download, device will copy the save data to SD card after each record. |
ASP command using new library
command |
parameters |
description |
|---|---|---|
AUAEC |
|
Open the AEC or not.
|
AUAECRUN |
|
|
AUNS/AUSPNS |
|
|
AUAGC/AUSPAGC |
|
Set up the auto gain control,
|